Health Problems Caused by Lack of Exercise in the Elderly
Contents [show]
If you’re an elderly person who isn’t getting enough exercise, you may be at risk for some serious health problems Learn more about the risks and how to stay healthy.
Checkout this video:
The elderly and lack of exercise
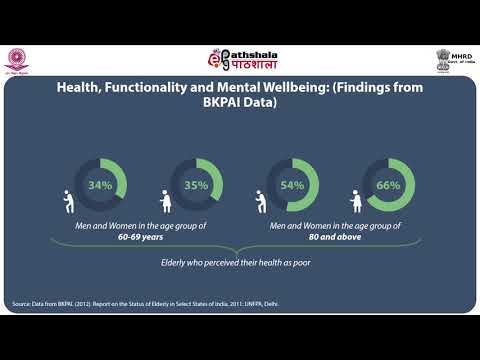
The elderly are at a higher risk for health problems caused by lack of exercise. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adults aged 65 and older should get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. However, only about one in four older adults meet this guideline.
Sedentary behavior is a major contributing factor to frailty and declining physical function in older adults. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to muscle weakness, joint problems, and decreased balance and coordination. Lack of exercise can also cause or worsen chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, arthritis, and high blood pressure.
Older adults who are unable to get regular exercise may be at risk for depression, social isolation, and cognitive decline. Additionally, lack of physical activity can cause weight gain, which can further compound health problems in the elderly.
If you are an older adult who is not getting enough exercise, talk to your doctor or a certified fitness professional about ways to safely start an exercise program. Regular physical activity can help improve your overall health and quality of life.
The dangers of a sedentary lifestyle
As we get older, our bodies become less able to handle physical activity. This can lead to a host of health problems, including obesity, heart disease, diabetes and even some forms of cancer.
One of the best ways to stay healthy as we age is to keep active. Unfortunately, many elderly people live a sedentary lifestyle, which can contribute to a whole host of health problems.
Obesity is one of the most common problems caused by lack of exercise in the elderly. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than one-third of adults aged 65 and over are obese. This is a major problem because obesity increases the risk of developing heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and some forms of cancer.
Exercise can help to prevent or manage these conditions. It also has other benefits, such as improving mental health reducing stress levels and increasing energy levels.
The benefits of exercise for the elderly
Exercise is important for people of all ages, but it’s especially important for older adults. Lack of physical activity can lead to a number of health problems, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and osteoporosis.
There are many benefits of exercise for the elderly. Exercise can help to improve balance and coordination, which can help to prevent falls. It can also increase muscle strength and endurance, which can help to improve mobility. Regular exercise can also help to reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
If you’re an older adult who is looking to start exercising, it’s important to talk to your doctor before starting any new fitness program. They can help you to create a program that is safe and effective for you.
The best exercises for the elderly
As we age, our bodies change and we become more susceptible to health problems. Lack of exercise can contribute to many of these problems, so it’s important to stay active as we age.
There are a number of exercises that are especially beneficial for the elderly. These include aerobic exercises (such as walking, biking, or swimming), strength-training (such as lifting weights), and balance-training (such as Tai Chi or Yoga).
Aerobic exercise is important for improving heart health and reducing the risk of conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Strength-training can help to reduce the risk of fractures and falls, and can also help to improve joint function. Balance-training can help to improve balance and coordination, which can reduce the risk of falls.
It’s important to talk to your doctor before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any health concerns Once you have the green light from your doctor, there are a number of ways to get started on an exercise program that’s right for you. You can join a gym or fitness class, go for walks or bike rides with friends or family members, or even do some exercises at home. What’s important is that you find an activity that you enjoy and stick with it!
How to get the elderly to exercise
As we age, our bodies become more sedentary. This is due to a number of factors, including a decrease in muscle mass, a decrease in bone density, and a decrease in the production of hormones that help to regulate our metabolism. This can lead to a number of health problems, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis.
One of the best ways to combat these problems is to encourage the elderly to exercise regularly. However, this can be difficult, as many of the elderly are not used to exercising and may not see the need to do so. Here are some tips on how to get the elderly to exercise:
-Start slow: Begin with gentle exercises that are easy to do and do not put too much strain on the body. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises as the person becomes more comfortable with them.
-Make it fun: Choose activities that the person enjoys doing. This could include walking, dancing, swimming, or gardening.
-Set realistic goals: Work with the person to set achievable goals that are specific and measurable. For example, “I want to be able to walk for 30 minutes three times per week” or “I want to be able to swim one length of the pool without stopping”.
-Make it social: Exercise is often more enjoyable when it is done with other people. If possible, find a friend or family member who is willing to exercise with the person. Alternatively, there are many exercise classes specifically designed for older adults that can provide both motivation and companionship.
The importance of exercise for cognitive health
As people age, they often become less active. This can lead to a number of health problems, including a decline in cognitive function. A new study has found that exercise can help to offset this decline.
The study, which was conducted by researchers at the University of British Columbia, looked at a group of sedentary older adults. The participants were divided into two groups: one that participated in a moderate-intensity exercise program for six months, and one that did not exercise.
The researchers found that the participants who exercised had better cognitive function than those who did not. They also found that the participants who exercised had more brain volume in the areas of the brain associated with memory and executive function.
These findings suggest that exercise can help to offset the declines in cognitive function that often occur with age. If you are an older adult, it is never too late to start exercising!
The link between lack of exercise and depression
Depression is a common problem in the elderly, and lack of exercise is a major contributor. If you are not getting enough exercise, you are at risk for developing depression. Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. In addition, lack of exercise can lead to weight gain, which can also contribute to depression.
Other health problems caused by lack of exercise include heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. These conditions are all more common in the elderly, and lack of exercise can increase your risk. Exercise lowers blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and helps to control blood sugar levels. All of these things help to reduce your risk of developing these conditions.
If you are not getting enough exercise, talk to your doctor about ways to get started. They can help you develop a safe and effective plan that will help you improve your health and reduce your risk of developing these conditions.
The impact of lack of exercise on physical health
The impact of lack of exercise on physical health is well-documented. In the elderly population, sedentary behavior is a major risk factor for chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and obesity. Even moderate levels of physical activity can help reduce the risk of these diseases.
The connection between lack of exercise and chronic illness
The link between lack of exercise and chronic illness is becoming increasingly clear. A sedentary lifestyle is a major risk factor for many diseases, including heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes, and arthritis. Even moderate amounts of exercise can help reduce the risk of these and other conditions.
Elderly adults are especially at risk for chronic illness due to their often sedentary lifestyle. This is compounded by the fact that many elderly adults also have other health conditions that make it difficult to be physically active. However, even small amounts of exercise can have a significant impact on their health.
There are many chronic illnesses that can be partially or completely prevented by regular exercise. These include heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes, arthritis, and osteoporosis. Exercise can also help improve mental health memory, and cognitive function. In addition, it can help reduce the risk of falls and fractures in the elderly.
There are a number of ways that older adults can get more exercise into their lives. Taking a brisk walk several times a week is a great way to start. Other options include swimming, biking, Tai Chi, yoga, or taking an exercise class at a local senior center. Whatever you choose, make sure it’s something you enjoy so you’ll stick with it!
The importance of staying active as you age
The importance of staying active as you age cannot be understated. Regular exercise has been shown to improve mental health reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases, and improve overall physical health. Unfortunately, many older adults do not get the recommended amount of exercise each week. This can lead to a number of health problems, including:
– obesity
– type 2 diabetes
– high blood pressure
– stroke
– heart disease
– arthritis
– osteoporosis
– falls and fractures
Exercise doesn’t have to be strenuous to be beneficial. Even moderate activity, like taking a brisk walk for 30 minutes each day, can make a significant difference in your health. So get up and get moving – your body will thank you for it!