Social Determinants of Health Affecting the Elderly
Contents
- Social Determinants of Health
- How Social Determinants of Health Affect the Elderly
- The Intersection of Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Care
- The Impact of Social Determinants of Health on Elderly Mortality
- The Relationship Between Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Quality of Life
- Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Access to Healthcare
- Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Housing
- Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Nutrition
- Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Social Isolation
- Addressing Social Determinants of Health to Improve Elderly Health Outcomes
Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) are the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age. They affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes. The goal of this blog is to provide information on the social determinants of health affecting the elderly.
Checkout this video:
Social Determinants of Health
The social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, and the wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life. These forces and systems include economic policies and systems, development agendas, social norms, social policies and political systems.
The social determinants of health are largely responsible for health inequities – the unfair and avoidable differences in health status seen within and between countries.
There is a growing body of evidence that demonstrates that the social determinants of health are the major drivers of poor health and that addressing them is essential to achieving equity in health. The evidence shows that:
-The higher someone’s socioeconomic position, the better their health
-Health inequities are avoidable and unfair
-Tackling the social determinants of health is essential to achieving equity in health
-A life course approach is needed to address the social determinants of health
How Social Determinants of Health Affect the Elderly
As people age, their health can be impacted by a variety of factors, including the social determinants of health. The social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work and age, and can include factors like socioeconomic status, education level, neighborhood and housing conditions, and access to healthcare. These factors can have a significant impact on an individual’s health, and can often be compounded for older adults.
Elderly adults may be more likely to live in poverty than younger adults, meaning they may have limited access to basic needs like food, shelter and healthcare. They may also be more likely to live alone or in isolated communities, which can lead to social isolation and loneliness. Additionally, older adults may have chronic health conditions that require ongoing treatment and care, which can be difficult to manage on a limited income.
All of these factors can contribute to poor health outcomes for older adults. They may be more likely to experience chronic diseases like heart disease or diabetes, and may have difficulty managing these conditions due to Limited access to resources. Additionally, social isolation and loneliness can lead to mental health problems like depression and anxiety.
It is important to address the social determinants of health in order to improve the overall health of older adults. By providing access to resources like affordable housing, nutritious food and quality healthcare, we can help ensure that older adults are able to age with dignity and good health.
The Intersection of Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Care
As our population continues to age, the issue of elderly care becomes increasingly important. A key factor in providing adequate care for seniors is understanding the social determinants of health that affect this population.
There are a number of social determinants of health that are particularly relevant to the elderly. These include factors such as economic stability, social isolation, and access to healthcare.
Economic stability is a major concern for many seniors. A recent study found that nearly one-third of American seniors are living in poverty. This can lead to a number of negative health outcomes, including poor nutrition, increased stress levels, and reduced access to healthcare.
Social isolation is another significant concern for seniors. A large number of older adults live alone, and this can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation. This can in turn lead to mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety. Additionally, social isolation can make it difficult for seniors to access essential services, such as transportation and grocery shopping.
Finally, access to healthcare is a critical issue for seniors. Many older adults do not have adequate insurance coverage, which can make it difficult to afford necessary medical care. Additionally, a lack of transportation can make it difficult for seniors to get to doctor’s appointments or the pharmacy.
The issues of social determinants of health are complex and multi-faceted. However, understanding these factors is essential in providing adequate care for our aging population.
The Impact of Social Determinants of Health on Elderly Mortality
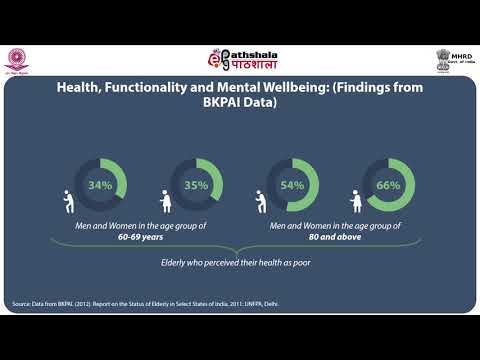
There is a growing body of research that suggests that social determinants of health (SDOH) have a significant impact on health outcomes, including mortality rates. The elderly are particularly vulnerable to the effects of SDOH, as they are more likely to experience poverty, social isolation, and barriers to healthcare.
A recent study by the CDC found that nearly one in four adults aged 65 or older live below the poverty line. This is especially troubling given that the elderly population is projected to nearly double by 2050. Social isolation is also a major problem for the elderly, with 26% of adults aged 65 or older reported feeling lonely.
Barriers to healthcare are another major concern for the elderly population. A study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that 24% of adults aged 65 or older have problems paying for medical care. In addition, 32% of adults aged 65 or older said they had difficulty getting transportation to doctor’s appointments.
The combination of poverty, social isolation, and barriers to healthcare can have a major impact on health outcomes. A study published in The Lancet found that SDOH are responsible for up to 40% of premature deaths in high-income countries. The study also found that the elderly are particularly susceptible to the effects of SDOH, with those aged 75 or older being twice as likely to die prematurely due to SDOH as those aged 25-49.
The findings of these studies emphasize the need for policies and programs that address the social determinants of health affecting the elderly population. Such policies could include increasing access to transportation and healthcare, reducing poverty rates, and combating social isolation through community programs and services.
The Relationship Between Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Quality of Life
There is a clear relationship between social determinants of health and elderly quality of life. The most important social determinant of health for the elderly is Income. Elderly people with higher incomes have better health, on average, than those with lower incomes. This is because higher-income elders can afford to live in better housing conditions, have better access to healthcare, and can afford healthier diets. Another important social determinant of health for the elderly is level of education. Elderly people with higher levels of education have better health, on average, than those with lower levels of education. This is because higher-educated elders are more likely to have higher incomes, which as we just discussed, leads to better health outcomes. Additionally, higher-educated elders are more likely to be aware of and make use of preventative health care measures. Finally, another important social determinant of health for the elderly is marital status. Married elders have better health, on average, than those who are not married. This is because married elders tend to have more social support than those who are not married. They also tend to have higher incomes and levels of education than those who are not married
Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Access to Healthcare
There are many social determinants of health that can affect the elderly population’s access to healthcare. Some of these determinants include income, education, employment, housing, and social support.
Income is a significant social determinant of health because it affects an individual’s ability to pay for medical care and prescriptions, as well as healthy food and other needs. Education can also play a role in someone’s ability to access healthcare, as those with higher levels of education may be more likely to have better jobs with health insurance
Employment can also be a social determinant of health, as those who are unemployed or underemployed may have difficulty affording healthcare. Housing is another social determinant of health, as those who live in substandard housing or homeless shelters may have reduced access to healthcare services. Social support is also a social determinant of health, as those who lack family or community support may have difficulty accessing care.
Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Housing
There are many social determinants of health that can affect the elderly housing situation. Some of these determinants include poverty, social isolation, and access to healthcare.
Poverty is a major social determinant of health. According to the US Census Bureau, 14.5% of seniors aged 65 and older live in poverty. This is nearly double the poverty rate for the general population (7.9%). Living in poverty can lead to poor housing conditions, lack of access to healthcare, and social isolation.
Social isolation is another social determinant of health that can affect the elderly. According to the AARP Foundation, one third of seniors aged 65 and older are socially isolated. Social isolation can lead to poor mental health declining physical health, and even mortality.
Access to healthcare is another social determinant of health that affects the elderly. According to the Kaiser Family Foundation, nearly 8 in 10 seniors aged 65 and older have at least one chronic condition, such as hypertension or diabetes. These chronic conditions can be expensive to treat and manage. Seniors who do not have access to adequate healthcare may not be able to get the care they need and this could lead to serious health complications or even death.
Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Nutrition
The social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work and age. They include factors like income, education, employment, housing and community environment. The WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health defines social determinants as “the structural drivers that shape the living conditions where we are born, grow, live, work and age.”
Elderly nutrition is a public health concern because poor nutrition can lead to frailty, falls and hospitalization. The social determinants of health can play a role in elderly nutrition by affecting a person’s access to healthy food and their ability to afford nutritious meals.
socioeconomic status, poverty and food insecurity are all social determinants of health that can affect elderly nutrition. Seniors who live in poverty are more likely to experience food insecurity, which is defined as inadequate or uncertain access to enough food for an active, healthy life. Food insecurity can lead to poor nutrition and diet-related chronic diseases such as obesity and diabetes.
According to the National Center for Elder Abuse (NCEA), 10% of seniors aged 60 and older have experienced some form of elder abuse. Financial exploitation is the most common type of elder abuse, followed by neglect and psychological abuse. Elder abuse can also take the form of physical or sexual abuse. Victims of elder abuse are more likely to suffer from malnutrition due to neglect or lack of access to nutritious food.
Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Social Isolation
Social Determinants of Health and Elderly Social Isolation
Social isolation is a public health issue among the elderly. It increases the risk for physical and mental health problems, and can lead to increased mortality. There are many social determinants of health that can contribute to social isolation among the elderly, including poverty, poor housing, lack of transportation, and poor access to healthcare. social service programs that focus on improving the social determinants of health for the elderly can help reduce social isolation and improve health outcomes.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health to Improve Elderly Health Outcomes
There is a growing body of evidence that social determinants of health (SDOH) play a significant role in health outcomes, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly. SDOH are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, and they include factors like income, education, housing, and community environments.
Numerous studies have shown that addressing SDOH can lead to improved health outcomes. For example, a recent study in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that interventions to address social needs were associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality among elders by 20%.
Given the clear link between SDOH and health outcomes, it is important for policy-makers and healthcare providers to identify opportunities to address SDOH in order to improve the health of older adults. Some potential strategies include:
– Increasing access to affordable housing
– Strengthening economic security for older adults
– Improving transportation options
– Creating age-friendly communities
– Enhancing social connectedness