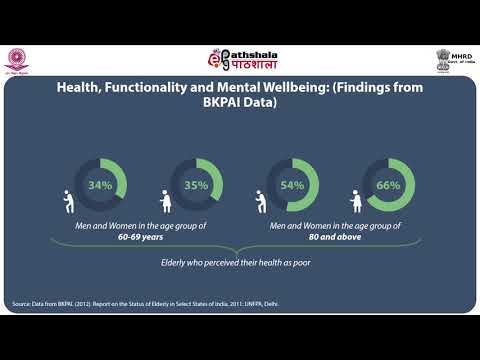
Health Care for Elderly People: What You Need to Know
Contents
Health care for the elderly is a growing concern. Learn what you need to know about health care for elderly people.
Checkout this video:
Introduction
As our population ages, more and more people are reaching the age where they will need some form of long-term care. This could be anything from in-home care to assisted living to full-time nursing care. While most people would prefer to age in their own homes, this is not always possible. According to a report from the National Institute on Aging, about 70% of people over the age of 65 will need some type of long-term care at some point in their lives.
There are a few things to take into consideration when trying to decide what type of care is best for you or your loved one. The first is the level of care that is needed. This can range from help with activities of daily living such as bathing and dressing, to more comprehensive care including medical and nursing services. The second is cost. Long-term care can be very expensive, and it’s important to understand what kind of coverage you have through insurance or government programs like Medicare before making any decisions.
In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at long-term care options for the elderly, as well as how to pay for them. We’ll also provide some tips on planning for your future long-term care needs so that you can make the best decisions for yourself or your loved ones.
The Need for Health Care
As we live longer, healthier lives, the number of elderly people is increasing. This presents both opportunities and challenges for society. One of the challenges is providing adequate health care for elderly people.
There are a number of reasons why health care for elderly people is important. First, as we age, we are more likely to experience chronic health problems. Chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, and arthritis are the leading causes of death and disability among older adults. Second, aging can lead to changes in our bodies that make us more vulnerable to injury and illness. For example, older adults are more likely to fall and break bones. And finally, many older adults take multiple medications that can interact in harmful ways.
A recent report by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) found that our current system of health care is not well designed to meet the needs of older adults. The IOM made a number of recommendations for improving health care for elderly people, including:
-Improving communication between patients and their health care providers
-Making sure that patients’ preferences are respected
-Providing patients with information about their treatment options
-Ensuring that patients have access to a continuum of care
-Improving coordination among different types of health care providers
-Encouraging patients to be active participants in their own care
The Types of Health Care
There are four types of health care: inpatient, outpatient, nursing home, and home health care.
-Inpatient care is when you stay at a hospital or other facility for treatment.
-Outpatient care is when you visit a doctor or other health care provider without staying overnight.
-Nursing home care is when you live in a facility that provides 24-hour nursing care.
-Home health care is when you receive health care services in your home.
The Cost of Health Care
Most people are unaware of the high cost of health care for elderly people. A recent study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that the average annual cost of health care for an elderly person is $5,441. This includes both medical and non-medical costs, such as long-term care.
There are several factors that contribute to the high cost of health care for elderly people. One is the fact that older adults tend to have more chronic health conditions than younger adults. They also often require more medications and have more frequent doctor and hospital visits.
Another factor that contributes to the high cost of health care for elderly people is the lack of insurance coverage. Medicare, the government-sponsored health insurance program for people 65 and over, only covers a portion of medical costs. Many elderly people also have private health insurance but their coverage is often not as comprehensive as Medicare. As a result, they often have to pay out-of-pocket for some or all of their medical expenses.
The high cost of health care for elderly people can be a financial burden on both individuals and families. If you are an elderly person or have an elderly family member, it is important to be aware of the potential costs and plan accordingly. There are several ways to reduce the cost of health care, including choosing a less expensive place to live, shopping around for doctors and hospitals, and using generic medications instead of brand-name drugs.
The Quality of Health Care
There are a number of factors influencing the quality of healthcare older people receive. One important factor is whether they have access to primary care. Research has shown that those who have regular contact with a primary care provider are more likely to receive preventive care and screenings, as well as coordinated and comprehensive care when they do become ill.
Other important factors influencing the quality of healthcare older people receive include the following:
– The number of health problems they have
– Their functional abilities
– The availability of caregivers
– The quality of the long-term care they receive
The Accessibility of Health Care
Most people in the United States have health insurance through their employers, but what happens when you retire? If you’re over 65, you’re eligible for Medicare, a federal health insurance program. You can also purchase private health insurance through companies like AARP or Blue Cross Blue Shield.
There are four parts to Medicare: Part A covers hospital stays, Part B covers doctor visits and outpatient care, Part C is a private health insurance option, and Part D covers prescription drugs. You can enroll in Medicare through the Social Security Administration or by visiting the website www.medicare.gov.
If you have a chronic illness or disability, you may also be eligible for Medicaid, a state-run program that provides health coverage for low-income individuals and families. Medicaid is different from Medicare in that it is means-tested (based on your income) and not everyone who is eligible for Medicare is automatically eligible for Medicaid. To find out if you qualify for Medicaid, contact your state’s Department of Health and Human Services.
The Availability of Health Care
Although our population is aging, the number of geriatricians has not increased commensurately. In 2012, there were only 7,600 geriatricians practicing in the United States—a number that is projected to increase to only 8,200 by 2030. Given that there are currently more than 46 million people over the age of 65 in the United States (and this number is projected to increase to 98 million by 2060), this shortage of geriatricians represents a significant challenge to our health care system.
There are a number of reasons for this shortage. First, medical students are not being trained in geriatrics. Of the more than 16,000 medical students who graduated from accredited US medical schools in 2016, only 764 (4.8%) completed a geriatrics fellowship—a postgraduate training program that is required for certification by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM). Second, many primary care physicians do not feel comfortable caring for older patients. According to a 2013 survey of primary care physicians, nearly 60% would not recommend their practices to someone seeking care for an elderly family member. Finally, our health care system is not designed to meet the needs of older patients. Most primary care practices have difficulty accommodating the complex needs of older patients with multiple chronic conditions and social needs.
One way to improve access to health care for older adults is to increase the number of geriatricians through workforce initiatives such as medical student scholarships and loan repayment programs. Another way is to support primary care physicians in caring for older patients through practice transformation initiatives such as those led by the Alliance for Better Health and other groups across the country.
The Responsibility of Health Care
As we age, our health care needs change. We may need more help from medical professionals to manage chronic conditions, take medications properly, and stay healthy and independent.
Although public programs like Medicare and Medicaid cover some of the costs of health care for older adults, out-of-pocket costs can still be a major financial burden. In fact, one in four adults aged 65 and older spend more than 10% of their income on out-of-pocket health care costs.
There are a few things you can do to reduce your health care costs as you age:
1. Get coverage through Medicare or Medicaid. If you qualify for either program, you can get help with paying for your health care costs.
2. Look into private insurance options. There are a number of private insurance plans that offer coverage for seniors. You may be able to get a discount on your premiums if you enroll in a plan through your employer or another group.
3. Take advantage of free or low-cost services. There are many organizations that offer free or low-cost health care services for seniors. You can often find these services at your local hospital, community center, or senior center.
4. Make healthy lifestyle choices. Healthy lifestyle choices can help you prevent chronic illnesses and reduce the need for costly medical treatments. Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise can all help keep you healthy as you age
The Impact of Health Care
Elderly people are one of the most vulnerable groups in our society when it comes to health care. They are more likely than any other age group to have chronic health problems, and their health care needs are often complex. This can make it difficult for them to get the care they need and put them at risk for serious health problems.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the difficulties elderly people face when it comes to health care. One of the most significant is the cost of care. Elderly people are more likely than other age groups to have fixed incomes, which can make it difficult for them to pay for care. In addition, they are often ineligible for government programs like Medicare and Medicaid, which can help offset the cost of care.
Another factor that contributes to the difficulties elderly people face when it comes to health care is access to care. Many elderly people live in rural areas, where there are fewer doctors and hospitals. This can make it difficult for them to get the care they need. In addition, many elderly people do not have transportation, which can make it difficult for them to get to doctor’s appointments or get prescriptions filled.
Finally, another factor that contributes to the difficulties elderly people face when it comes to health care is their overall health. Elderly people are more likely than other age groups to have chronic health problems, which can make it difficult for them to receive the care they need. In addition, their overall health can decline as they age, making it more difficult for them to recover from illness or injury.
The difficulties elderly people face when it comes to health care can have a serious impact on their overall health and wellbeing. It is important that we do everything we can to ensure that they receive the care they need and deserve
The Future of Health Care
The future of health care is a hot topic these days. With the baby boomers starting to reach retirement age, and with the costs of health care skyrocketing, there is a lot of discussion about how to ensure that everyone will be able to receive the care they need.
There are many different ideas about what the future of health care should look like, but one thing is certain: the current system is not sustainable. The cost of health care is rising much faster than inflation, and it is becoming increasingly difficult for people to pay for their own care.
One proposal that has been gaining traction lately is the idea of a single-payer health care system. In this system, everyone would be covered by a single insurance provider (likely the government). This would eliminate the need for people to buy private insurance, and it would also help to control costs by negotiating lower prices with providers.
Another proposal that has been gaining support is the idea of allowing people to buy health insurance across state lines. This would create more competition among insurers and force them to offer lower prices.
Whatever the future of health care looks like, it is clear that something needs to be done to reform the system. The current system is simply not affordable or sustainable in the long term.